☰
In order to develop Java applications you need the Java Software Developer Kit (JDK) installed. The JDK includes tools useful for developing and testing programs written in the Java programming language and running on the Java platform.Java is freely available on Oracle's Website. Download the latest version of JDK (Java Development Kit) on your machine. The most current version at the time of writing is the Java 8 SDK.
Latest version of Java can be downloaded from Java Website
http://www.oracle.com/technetwork/java/javase/downloads/jdk8-downloads-2133151.htmlOnce java is downloaded, it can be installed like any other software (.exe) in your Windows system.Once you have installed Java on your machine you would need to set environment variable to point to correct installation directory.
An Environment variable is an object on a computer that stores a value(key-value pair), which can be referenced by one or more software programs in Windows.
If you are saving the java source file inside the jdk/bin directory, path is not required to be set because all the tools will be available in the current directory. But If you are having your java file outside the jdk/bin folder, it is necessary to set path of JDK. After installing the software, the JDK directory will have the structure shown below.
You can run Java applications just fine without setting the PATH environment variable. Or, you can optionally set it as a convenience.
Set the PATH environment variable if you want to be able to conveniently run the executables (javac.exe, java.exe, javadoc.exe, and so on) from any directory without having to type the full path of the command. If you do not set the PATH variable, you need to specify the full path to the executable every time you run it, such as:
C:\Java\jdk1.7.0\bin\javac MyClass.java
The PATH environment variable is a series of directories separated by semicolons (;). Microsoft Windows looks for programs in the PATH directories in order, from left to right. You should have only one bin directory for the JDK in the path.
It is useful to set the PATH environment variable permanently so it will persist after rebooting. To make a permanent change to the PATH variable, use the System icon in the Control Panel. The precise procedure varies depending on the version of Windows:
PATH environment variable and select it. Click Edit. If the PATH environment variable does not exist, click New.PATH environment variable. Click OK. Close all remaining windows by clicking OK.PATH environment variable and select it. Click Edit. If the PATH environment variable does not exist, click New.PATH environment variable. Click OK. Close all remaining windows by clicking OK.PATH environment variable and select it. Click Edit. If the PATH environment variable does not exist, click New.PATH environment variable. Click OK. Close all remaining windows by clicking OK.You can run the JDK just fine without setting the PATH variable, or you can optionally set it as a convenience. However, you should set the path variable if you want to be able to run the executables (javac, java, javadoc, and so on) from any directory without having to type the full path of the command. If you do not set the PATH variable, you need to specify the full path to the executable every time you run it, such as:
% /usr/local/jdk1.7.0/bin/javac MyClass.java
To find out if the path is properly set, execute:
% java -version
This will print the version of the java tool, if it can find it. If the version is old or you get the error java: Command not found, then the path is not properly set.
To set the path permanently, set the path in your startup file.
For C shell (csh), edit the startup file (~/.cshrc):
set path=(/usr/local/jdk1.7.0/bin $path)
For bash, edit the startup file (~/.bashrc):
PATH=/usr/local/jdk1.7.0/bin:$PATH
export PATH
For ksh, the startup file is named by the environment variable, ENV. To set the path:
PATH=/usr/local/jdk1.7.0/bin:$PATH
export PATH
For sh, edit the profile file (~/.profile):
PATH=/usr/local/jdk1.7.0/bin:$PATH
export PATH
Then load the startup file and verify that the path is set by repeating the java command:
For C shell (csh):
% source ~/.cshrc
% java -version
For ksh, bash, or sh:
% . /.profile
% java -version
The CLASSPATH variable is one way to tell applications, including the JDK tools, where to look for user classes. (Classes that are part of the JRE, JDK platform, and extensions should be defined through other means, such as the bootstrap class path or the extensions directory.)
The preferred way to specify the class path is by using the -cp command line switch. This allows the CLASSPATH to be set individually for each application without affecting other applications.Setting the CLASSPATH can be tricky and should be performed with care.
The default value of the class path is ".", meaning that only the current directory is searched. Specifying either the CLASSPATH variable or the -cp command line switch overrides this value.
To check whether CLASSPATH is set on Microsoft Windows NT/2000/XP, execute the following:
C:> echo %CLASSPATH%
On Solaris or Linux, execute the following:
% echo $CLASSPATH
If CLASSPATH is not set you will get a CLASSPATH: Undefined variable error (Solaris or Linux) or simply %CLASSPATH% (Microsoft Windows NT/2000/XP).
To modify the CLASSPATH, use the same procedure you used for the PATH variable.
To check if your java is installed properly open Command Prompt . To open command prompt write “CMD” in run command and hit enter. In the command prompt window write “java -version“. If your java is installed properly and all environment variables are configured correctly it will show the version of Java installed . Information reflected on the command prompt will be like
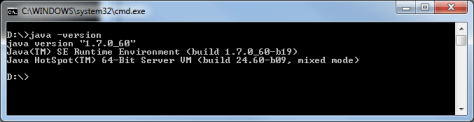
If there is any problem while installing or in setting up the environment variable, output on command prompt will be like
'java' is not recognized as an internal or external command,operable program or batch file.